=> Amazon Reviews of the Duality of Time... ok and other reviews page . Review by: Jonah Erickson Thought-Provoking, Challenging View of Reality and Existence March 10, 2018 The premise of the book is simple: time exists in a "real," vacuum state which we then experience in a latent, secondary state. In other words, by removing all ...
=> ULTIMATE SYMMETRY - III.3 Equivalence Principle and General
Relativity... ve mass. Therefore, a closed system is closed only when we include all its contents of mass and energy (including kinetic and radiation) as well as the background space itself, which is the vacuum state , and the momentum of all these constituents is either , when they are re-created in th ...
=> ULTIMATE SYMMETRY - III.2.9 Method IV (complex momentum and
energy-momentum relation)... e normal time, or physical motion, is interrupting the real creation, which is causing the disturbance and curvature of the otherwise infinite homogeneous Euclidean space that describes the vacuum state . Therefore, to obtain the relativistic energy-momentum relation from equation 3.17, we ...
=> ULTIMATE SYMMETRY - III.2.3 Method II (generating mass in
the inner time):... II (generating mass in the inner time): We explained in section III.3.3 above how the Duality of Time Theory provides a fundamental mass generation mechanism in addition to its super-fluid vacuum state where mass can be generated via the interaction with this physical vacuum. Hence we can ...
=> ULTIMATE SYMMETRY - II.1.5 Higgs Mechanism... , or momentum, becomes absolutely zero, both as the object s total velocity and any vector velocities of its constituents, and this corresponds to absolute zero temperature (). This dynamic vacuum state is therefore a super fluid, which is a perfect Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC), since it ...
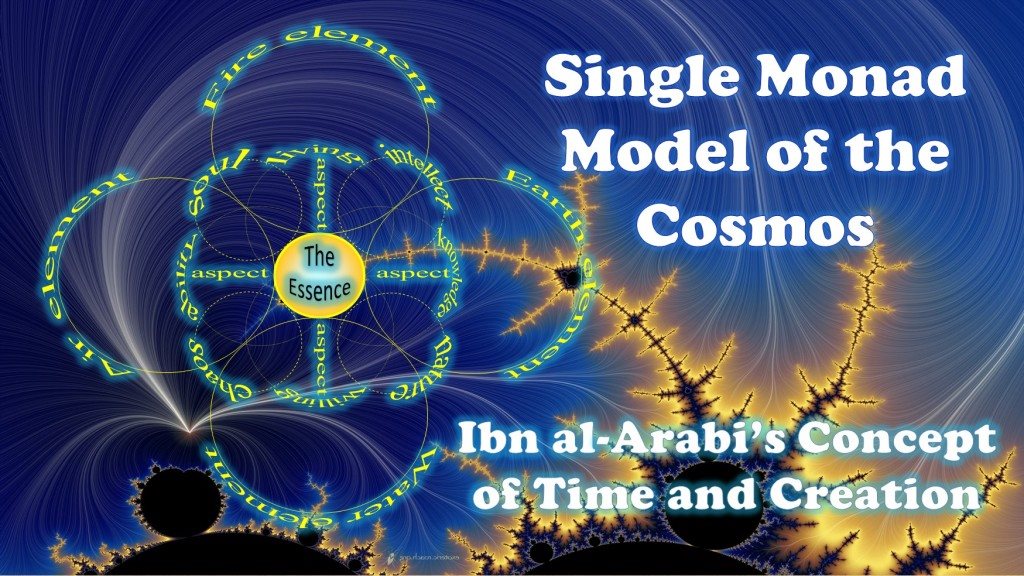
=> ULTIMATE SYMMETRY - CHAPTER II: SUPER SYMMETRY... psychical worlds, or the meeting of the two lights alluded to in the opening epigraph at the top of this chapter. The state of Water , from which Allah made everything living, is the vacuum state , which is the ground state of matter, since the physical particles are its excitations ...
=> ULTIMATE SYMMETRY - I.3.2 Breaking of Symmetry... e spontaneous breaking of symmetry occurs when only the ground state of the system becomes no more invariant under some circumstances, so the symmetry is broken for perturbations around the vacuum state even though the entire Lagrangian retains that symmetry, and this breaking may also be ...
=> ULTIMATE SYMMETRY - I.2.3 Fractal Dimensions and the
Emergence of Time... -fractal and equals to the dynamic ratio of inner to outer times, because spatial dimensions alone, as an empty homogeneous space, are complete integers, while tractability arises when this vacuum state starts oscillating in the outer time, which causes all types of evolving elementary par ...
=> ULTIMATE SYMMETRY - i.4 The Principle of Love and
Stationary Action... the physical and psychical worlds, , , respectively, we get the two folds of super-symmetry. The current laws of physics are concerned only with the first half, of the physical world whose vacuum state is , and that s why we are faced with the various problems, such as the arrow-of-time, ...
=> THE DOT POSTULATE - 6.3. The Equivalence Principle of General Relativity... ve mass. Therefore, a closed system is closed only when we include all its contents of mass and energy (including kinetic and radiation) as well as the background space itself, which is the vacuum state , and the momentum of all these constituents is either , when they are re-created in th ...
=> THE DOT POSTULATE - Method IV (complex momentum and energy-momentum relation)... e normal time, or physical motion, is interrupting the real creation, which is causing the disturbance and curvature of the otherwise infinite homogeneous Euclidean space that describes the vacuum state . Therefore, to obtain the relativistic energy-momentum relation from equation 19, we s ...
=> THE DOT POSTULATE - Method II (generating mass in the inner time):... d II (generating mass in the inner time): We explained in section 5.5 above how the Duality of Time Theory provides a fundamental mass generation mechanism in addition to its super-fluid vacuum state where mass can be generated via the interaction with this physical vacuum. Hence we can ...
=> TIME CHEST - 3.4.2 The Equivalence Principle of General
Relativity... ve mass. Therefore, a closed system is closed only when we include all its contents of mass and energy (including kinetic and radiation) as well as the background space itself, which is the vacuum state (c, 0) , and the momentum of all these constituents is either p=mc , when they are re-c ...
=> THE DOT POSTULATE - 5.1. The Genuinely-Complex Time-Time Frame:... omentum, becomes absolutely zero, both as the object’s total velocity and any vector velocities of its constituents, and this corresponds to absolute zero temperature (0 K ). This dynamic vacuum state is therefore a super-fluid, which is a perfect Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC), since it ...
=> ULTIMATE SYMMETRY - II.1.4 Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking... rangian retains that symmetry. The symmetry group can be discrete or continuous, but if the system contains only a single spatial dimension, then only discrete symmetries may be broken in a vacuum state of the full quantum theory, although a classical solution may break a continuous symmet ...
=> ULTIMATE SYMMETRY - II.3.2 Super Symmetry in Strings Theory
and Extra Dimensions... d on Strings Theory, physicists typically begin by specifying a shape for the extra dimensions of space-time. Each of these different shapes corresponds to a different possible Universe, or vacuum state, with a different collection of particles and forces. String theory as it is currently ...
=> TIME CHEST - 3.3.3 The Two Arrows of Time... ite and inert Euclidean space (without time), because its dimensions are continuous, or uninterrupted. The metaphysical entities of the Universe are sequentially oscillating between the two vacuum states (as Euclidean spaces or normal complex numbers): (c, 0) and (c, c) , while collectivel ...
=> ULTIMATE SYMMETRY - II.4.2 The Two Arrows of Time... ite and inert Euclidean space (without time), because its dimensions are continuous, or uninterrupted. The metaphysical entities of the Universe are sequentially oscillating between the two vacuum states (as Euclidean spaces or normal complex numbers): and , while collectively they a ...
=> Solving the Arrow of Time Problem Based on the Duality of Time Theory... ite and inert Euclidean space (without time), because its dimensions are continuous, or uninterrupted. The metaphysical entities of the Universe are sequentially oscillating between the two vacuum states (as Euclidean spaces or normal complex numbers): (c, 0) and (c, c), while collectively ...
=> THE DOT POSTULATE - 5.2. The Two Arrows of Time:... ite and inert Euclidean space (without time), because its dimensions are continuous, or uninterrupted. The metaphysical entities of the Universe are sequentially oscillating between the two vacuum states (as Euclidean spaces or normal complex numbers): and , while collectively they appea ...
=> The Duality of Time Theory... ite and inert Euclidean space (without time), because its dimensions are continuous, or uninterrupted. The metaphysical entities of the Universe are sequentially oscillating between the two vacuum states (as Euclidean spaces or normal complex numbers): ( c , 0 ) and ( c , c ) , while colle ...